Clinical Study Insights

A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study to Evaluate the Modulatory Effect of Lutein and Zeaxanthin Supplementation on Macular Pigment Optical Density (MPOD), Glare Disability and Photo Stress in Healthy Subjects
120 healthy adults (45-65 years)
• 20 mg (per day)
At Day 0, 45, and 90 included MPOD measurement, glare disability tests, photo-stress recovery, and plasma lutein/zeaxanthin quantification.
Changes in MPOD, glare disability, photo-stress recovery time, and plasma lutein/zeaxanthin levels.
Safety assessment through biochemical and haematological analyses.
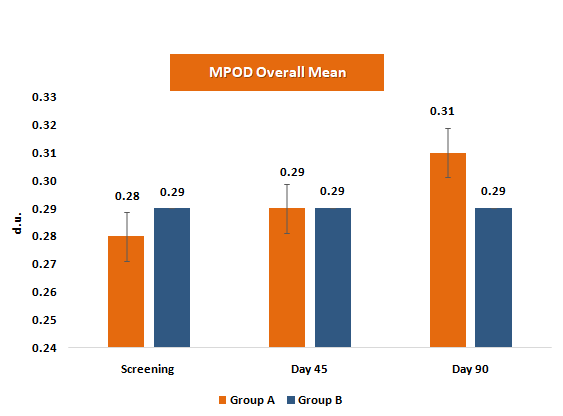
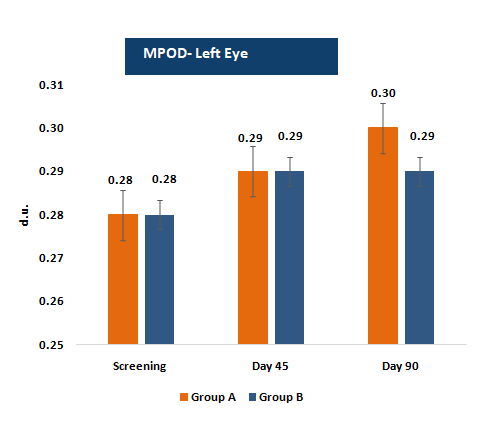
Macular Pigment Optical Density (MPOD)
MPOD represents the concentration of macular carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin in the retina, serving as a biomarker for visual health and protection against blue-light-induced oxidative damage.
MPOD levels were assessed using Heterochromatic Flicker Photometry (HFP)
Macular Pigment Optical Density (MPOD)

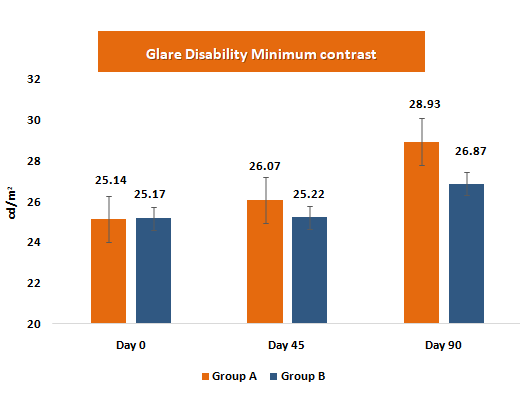
Glare disability assesses the reduction in visual performance or clarity when exposed to bright light. Improvement in glare disability reflects enhanced visual comfort and functional vision under high-luminance conditions, which are sensitive indicators of the protective effect of macular pigments.
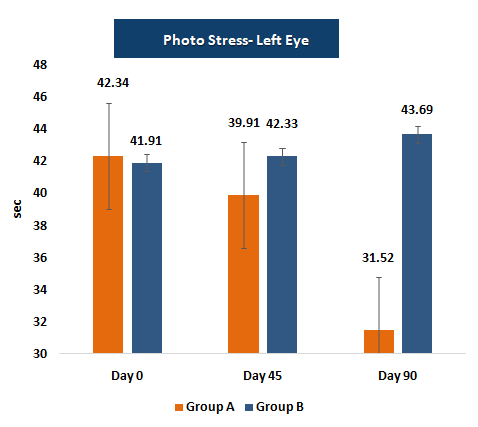
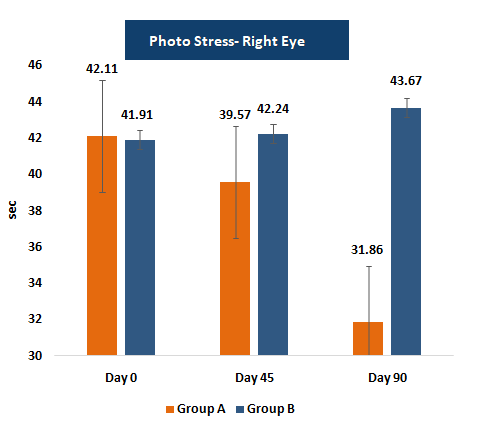
PSRT measures the duration required for vision to recover after exposure to a bright light source.
A shorter recovery time indicates improved retinal resilience and photoreceptor function, providing functional evidence of enhanced visual performance due to supplementation.
Photo-Stress Recovery Time (PSRT)
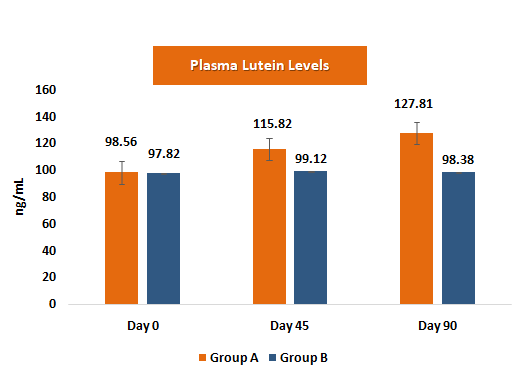
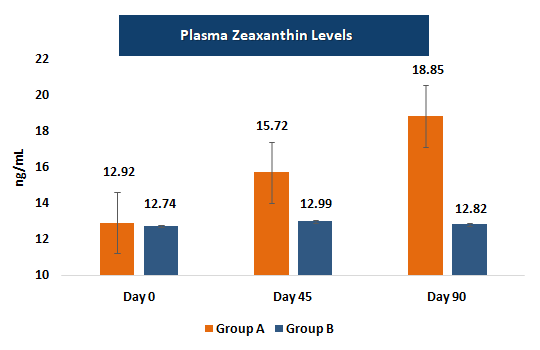
Plasma concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin serve as biochemical markers of systemic absorption and bioavailability. Increases in these levels correlate with enhanced macular deposition and visual benefits, supporting the biological plausibility of efficacy findings.
Participant’s experience strongly aligned with the study outcomes. Adverse effects were minimal and comparable between groups (Group A: 3.6%, Group B: 3.7%, p = 0.8905), confirming excellent safety.
Perceived benefits were markedly higher in Lutenic® Group:
✓ No major adverse events occurred, and both study groups were comparable in vital signs, physical exams, and laboratory findings.
- • Hematology, RFT, LFT, Lipid profile, and Urine analysis remained within normal limits across all visits.
- • No clinically significant changes from baseline to Day 90.
- • Confirms no biochemical or organ-function concerns.
- • Temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure were stable at all time points.
- • No abnormal or clinically relevant shifts observed.
- • Overall, the investigational product demonstrated excellent safety and tolerability.
- • Daily supplementation with 20 mg lutein–zeaxanthin for 90 days significantly improved visual function in healthy adults (Group A).
- • MPOD increased steadily at Day 45 and Day 90, with statistically significant within-group improvements and clinically meaningful percentage gains (~3.6% at Day 45 to ~10.7% at Day 90).
- • Glare tolerance improved by +3.79 (minimum contrast) and +3.71 (maximum contrast) units, compared with +1.70 and +1.13 units in the placebo group.
- • Photo-stress recovery time decreased to ~32.2 seconds in the supplemented group versus ~43.7 seconds in placebo.
- • Plasma levels increased substantially, with lutein rising by ~29.7% and zeaxanthin by ~45.9%; plasma levels in the placebo group remained essentially unchanged.
- ✓ The supplementation was well tolerated and effectively supported macular health and visual performance under light-induced stress.
Copyright © 2026 Lutenic® | All Rights Reserved.